Some days ago I wondered how I could add a location functionality in my Django web app that would enable users know the locations and distance of other registered users from them, therefore generating a dashboard for "User Near You". I definitely knew I was going to use one of the python GIS (Geographical Information System) libraries but which one? and which was supported by the Django Framework? This was when I stumbled upon GeoDjango.
WHAT IS GEODJANGO?
GeoDjango is an included contrib module to make easy GIS (Geographic Information System) web apps with location-based services. GeoDjango provides a toolbox of utilities for building GIS web applications and also bindings to popular spatial libraries such as GEOS, GDAL, and GeoIP, which can be used separately without Django in any Python application or interactively in the shell.
TIME TO GET OUR HANDS DIRTY

Prerequisites: Python , GDAL , POSTGRESQL ,POSTGIS ,Django
SETTING UP OUR DJANGO APP
Lets start by creating a django project. From our terminal we will run the following:
django-admin startproject GEOPROJECT
cd GEOPROJECT
django-admin startapp APP
cd APP
mkdir templates
Here we created initialized our Django project named "GEOPROJECT" then changed the directory to our project where we initialized our app named "APP" then created a new directory with our APP named templates where we will store our template files.
Create a new file urls.py at GEOPROJECT/APP/ and add the following lines of code:
from django.urls import path, include
from . import views
app_name = "APP"
urlpatterns = [
path("", views.index, name="index"),
]
In the code above defined our index url where we will display our users location information.
Edit your GEOPROJECT/GEOPROJECT/settings.py file
#if you are using a windows machine and installed GDAL from OSGEO4W add the following code after import os
if os.name == 'nt':
import platform
OSGEO4W = r"C:\OSGeo4W"
if '64' in platform.architecture()[0]:
OSGEO4W += "64"
assert os.path.isdir(OSGEO4W), "Directory does not exist: " + OSGEO4W
os.environ['OSGEO4W_ROOT'] = OSGEO4W
os.environ['GDAL_DATA'] = OSGEO4W + r"\share\gdal"
os.environ['PROJ_LIB'] = OSGEO4W + r"\share\proj"
os.environ['PATH'] = OSGEO4W + r"\bin;" + os.environ['PATH']
from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib
os.environ["PATH"] += os.pathsep + get_python_lib() + '\\osgeo'
Add APP and django.contrib.gis to INSTALLED_APP
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'django.contrib.gis',
'APP',
]
Edit TEMPLATES
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
Edit DATABASES configurations with your Postgresql details
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.contrib.gis.db.backends.postgis',
'NAME': 'db_name',
'USER': 'user',
'PASSWORD': 'db_passowrd',
'HOST': 'localhost'
}
}
Now Edit the urls.py file at GEOPORJECT/GEOPROJECT/urls.py to
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include("APP.urls")),
]
In the code above we included our urls defined in our APP to the root urls.py
Now lets create our models. Edit your GEOPROJECT/APP/models.py to
from django.contrib.gis.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class UserProfile(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User,on_delete=models.CASCADE)
name=models.TextField()
geo_location = models.PointField(srid=4326, null=True,blank=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
In the code above we created a model for creating and saving user data and location to our database.
Now lets run the commands below from our project root directory to migrate our databse
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
NB:Please make sure you have Postgis enabled before running this command
If the migrations above ran successfully without throwing any error then you are good to go.
Now lets add our models to the admin site, edit your admin.py at GEOPROJECT/APP/admin.py
from django.contrib import admin
from . models import UserProfile
# Register your models here.
admin.site.register(UserProfile)
Creating User Data
We can now add user data to our models from our admin site. First off ,lets create a superuser from terminal by running the below command and entering the required information
python manage.py createsuperuser
Once we have created our user we can now access the admin site at 127.0.0.1:8000//admin on our browser by entering the information we used to create the superuser above
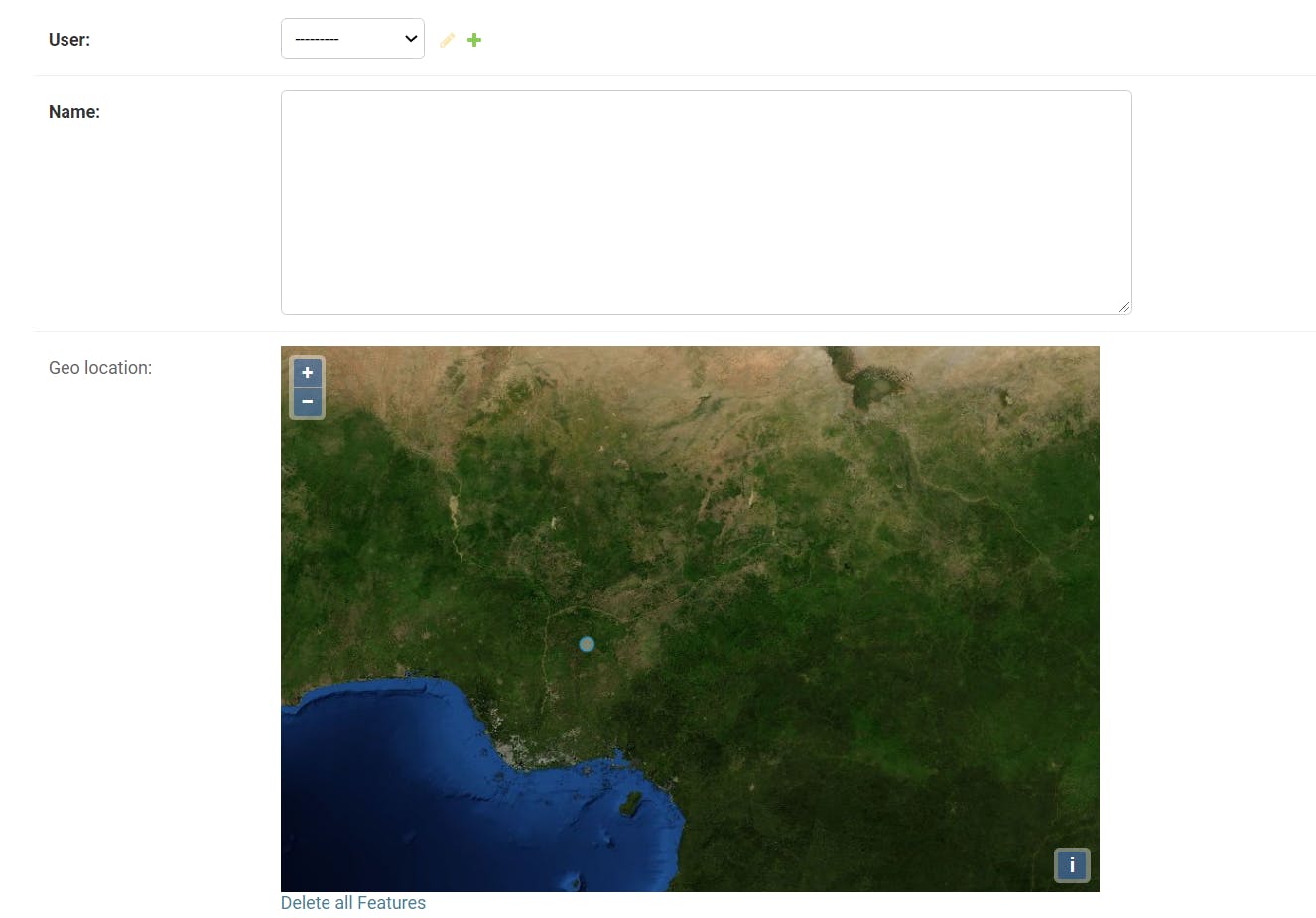
After Logging in click on UserProfile and proceed to adding user information and location

Enter info and location and save. Do this for four more users
Creating our Views
Next we create our views in our views.py file at GEOPROJECT/APP/views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from APP.models import UserProfile
from django.contrib.gis.measure import D
from django.db.models import Q
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
school = UserProfile.objects.first()
#Assume first object is required School
close_by=UserProfile.objects.filter(geo_location__distance_lte=(school.geo_location, D(m=100)))
#query for school 10 metres from
mid_distance=UserProfile.objects.filter(geo_location__distance_lte=(school.geo_location, D(mi=10)))
#query for school 10 miles from you
far=UserProfile.objects.filter(geo_location__distance_lte=(school.geo_location, D(km=10)))
#query for school 10 kilometres from you
within_range=UserProfile.objects.filter(Q(geo_location__distance_gte=(school.geo_location, D(km=5)))
& Q(geo_location__distance_lte=(school.geo_location, D(km=10))))
#query for school within a distance of 5km to 10km
context={"close_by":close_by,"mid_distance":mid_distance,"far":far,"within_range":within_range}
return render(request,"index.html",context)
Above we created our index view and called the first object from our UserProfile Object then queried the database for the various conditions stated, mappped the results in our context and returned all data to our index view.
We will then move on to creating our index.html file at our GEOPROJECT/APP/templates directory where we will display the location of the users and filtered queries
<html>
<style>
table,
td {
border: 1px solid #333;
}
thead,
tfoot {
background-color: #333;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
<table style="width:100%">
<center><h2>Users Near You</h2></center>
<tr>
<th>Users Close By</th>
<th>Users Not Too Far(Mid-Distance)</th>
<th>Users Far From You</th>
<th>Users Within 5km to 10km from You</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><li>{% for i in close_by %}User:{{i.name}}
Location:{{i.geo_location}}{% endfor %}</li></td>
<td><li>{% for i in close_by %}User:{{i.name}}
Location:{{i.geo_location}}{% endfor %}</td>
<td>{% for i in far %}<li>User:{{i.name}}
Location:{{i.geo_location}}</li> {% endfor %}</td>
<td>{% for i in within_range %}User:{{i.name}}
Location:{{i.geo_location}}{% endfor %}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</html>
Running Our Project
Finally We can now run our project with the below command
python manage.py runserver
Now Go to 127.0.0.0:8000 on your browser to view user locations
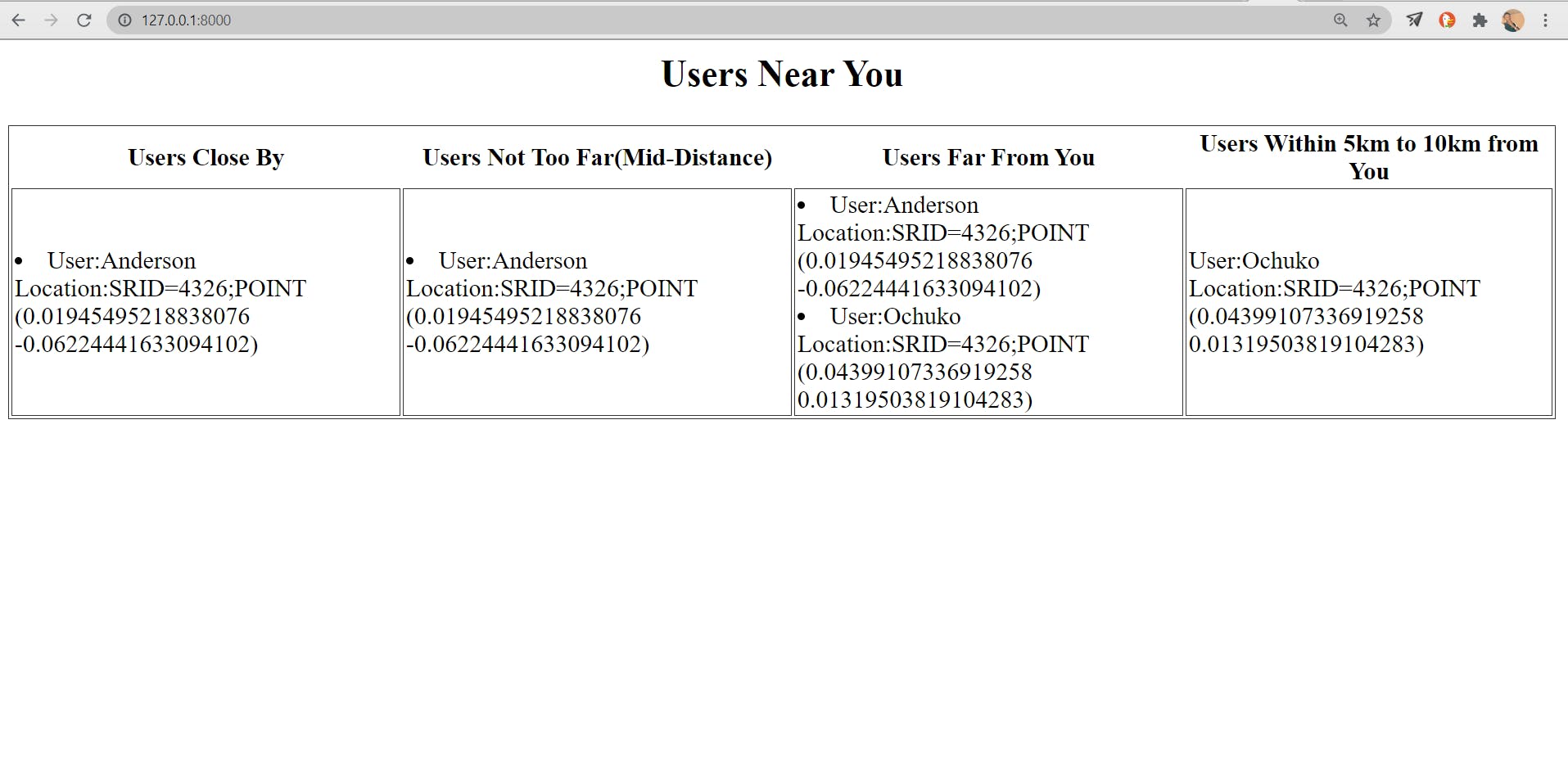
Hurray 🎉 our app is running
CONCLUSION
We learnt about GEODJANGO and when to use it
We learnt how to implement GEODJANGO in Django App
We learnt how to create our POSTGIS model for our Django App
And you got to read my first article on hashnode :)
In the future , I might write a second part of this article on how to to show map data and user locations on the map using leaflet and .kml files.
